There are many ways to earn additional income. Some people invest in company stocks, others deposit money into savings accounts, and there are those who invest in digital currencies.
Cryptocurrencies offer broad opportunities for generating profit in various ways. Some methods require almost no effort from users, yet they still allow them to earn money. One of these methods is cryptocurrency staking, which is the focus of this article. For more details on other ways to earn income from digital currencies, how to maximize potential earnings, and minimize risks, refer to the article "Cryptocurrency Basics."
How to earn with cryptocurrencies
There are several ways to earn with digital currencies, broadly divided into active and passive income methods. As the names suggest, active income requires significant effort, while passive income involves minimal actions from the user.
Active income methods
- Trading
One of the most popular ways to earn with cryptocurrencies. It involves speculative trading based on price fluctuations. This method requires thorough preparation, a well-developed strategy, and substantial time investment. For many, it becomes a full-time profession.
Arbitrage
A type of trading that involves buying and selling cryptocurrencies on different platforms. The goal is to buy coins at a lower price on one platform and sell them at a higher price on another. This method also demands a considerable amount of time.
- Mining
The process of earning new coins by solving complex mathematical problems. Although the calculations are performed by powerful specialized equipment, users need to purchase, configure, and maintain this equipment themselves.
- Affiliate Programs
This refers to bringing new users to a cryptocurrency platform. Users need to promote their referral link on social media or other websites to attract as many people as possible.
- Blockchain games
A fun and engaging way to earn. Players need to purchase characters and game items, upgrade them, participate in competitions, and win rewards. However, it also requires a significant time commitment.
Passive income methods
Now let us explore passive income opportunities that require minimal effort from users:
- Investments (Holding)
Similar to traditional investments, users buy digital currencies and hold them until their value increases. This method requires careful selection of assets and the creation of a diverse investment portfolio.
- Staking
Involves locking a specific amount of cryptocurrency in an account to support the platform's operations. These funds cannot be used for other purposes, but users earn rewards for staking their tokens.
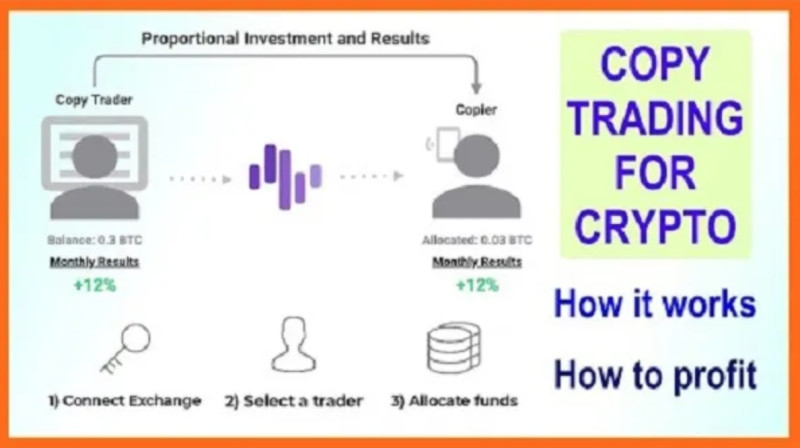
- Copy Trading
A form of trading where an experienced trader's transactions are automatically replicated in the follower's account. Users only need to subscribe to a trader and pay a commission for their services.
- Lending
Lending digital currencies to earn interest. Specialized platforms enable this by acting as intermediaries, offering loans from one user to another. Alternatively, users can directly lend their coins to others.
- Airdrops
A marketing strategy by developers of new cryptocurrencies that involves distributing coins for free. To receive coins, users typically perform simple tasks such as following social media accounts or sharing posts.
- Cloud Mining
A type of mining where users rent equipment from specialized companies instead of owning it. This eliminates the need for maintenance or electricity costs while still generating income.
Cryptocurrencies suitable for staking
Not all cryptocurrencies are suitable for staking. This depends primarily on the consensus algorithm used by the blockchain. The most common algorithms are Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Work (PoW), with PoS being more prevalent in newer blockchains.
What is the difference between PoS and PoW? In PoW-based chains, miners verify transactions and add them to blocks by solving complex mathematical problems, hence the name "proof of work." Miners are rewarded with new coins for their efforts.
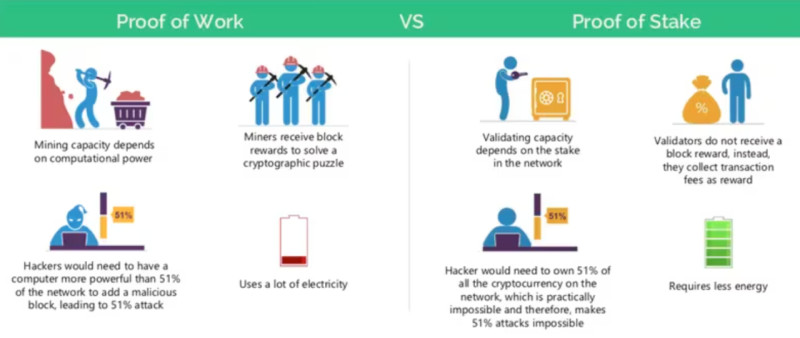
In PoS-based chains, validators perform the same role. To become a validator, one must lock a certain amount of the chain's native cryptocurrency, a process known as staking. Validators are rewarded for this contribution.
Staked funds serve two purposes. They maintain the network's functionality and act as collateral. If a validator records incorrect data or performs poorly, they risk losing their staked funds.
Each blockchain has its own staking rules for validators. Usually, becoming a validator requires setting up a special chain node, or node, which is a part of the blockchain's infrastructure under the PoS algorithm. This requires technical knowledge and a significant amount of capital.
Alternatively, intermediary services like exchanges or staking pools act as validators. These services allow users to stake funds and earn income proportional to their contribution without dealing with the technical complexities.
What is cryptocurrency staking?
We have mentioned the term "staking" several times, so now it is time to understand what it means and how it works. The word "staking" comes from the English word "stake," meaning "share," which refers to holding a certain amount of coins of a particular cryptocurrency.
Every blockchain has its native currency, used to pay fees and perform other functions. Staking involves acquiring and locking up a specified amount of these native tokens, for which the user receives rewards.

Rewards are usually calculated as a percentage of the staked amount. This percentage can vary significantly between cryptocurrencies. Some offer around 4%-5%, others 12%-15%, and some even exceed 20%.
There are two main types of staking:
- Fixed Staking
Coins are locked for a predetermined period, usually several months, during which the user cannot access their funds. Fixed staking typically offers higher returns due to the increased risk involved.
- Flexible Staking
There is no set locking period. Investors can withdraw their funds anytime, but rewards are credited periodically, such as once a month, rather than daily.
Staking helps projects build strong and loyal communities that support their operations and are invested in their future development. It also allows participants to engage in governance by voting and even submitting their ideas.
The locking period can also affect the weight of a holder’s vote. Typically, the longer the staking period, the more significant the user’s influence in decision-making.
How staking works
Cryptocurrency staking can be compared to a bank deposit. A customer deposits money into a bank account, earning interest while the bank uses the funds for purposes like lending.
However, interest rates for bank deposits are often low and depend on the currency of the account. The interest rate on bank deposits often does not exceed 5% per year. Nevertheless, such deposits are considered reliable because they are insured. In the event of a bank's bankruptcy, the state guarantees the return of funds.
In contrast, staking digital currencies offers much higher returns, but it comes with significantly greater risks. Cryptocurrencies lack a central authority to regulate their activities. Consequently, in the event of a hacking attack, all user funds could be irretrievably stolen.
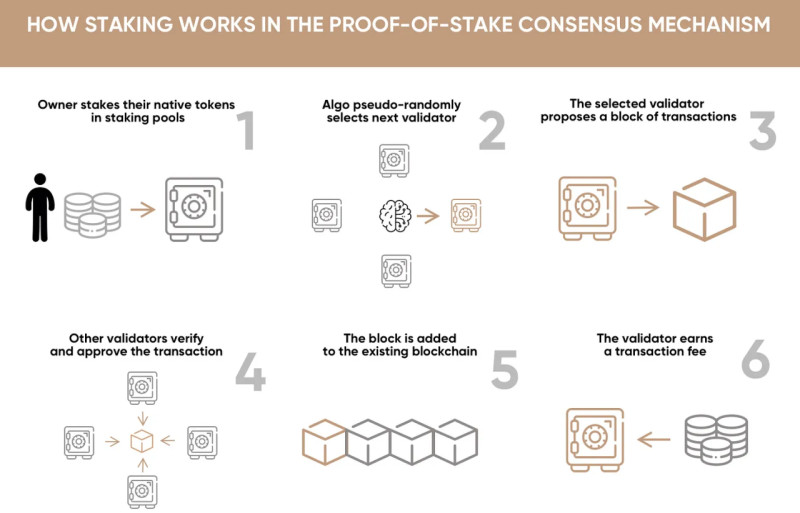
Now, let us understand how staking works. When adding each block to the chain, one validator is chosen automatically. The system evaluates the stake size—the number of locked coins—and the duration of the lock, selecting a validator accordingly.
Typically, those who lock more coins for a longer period have higher chances of being selected. Validators earn new coins for adding each block to the network, which introduces additional units of a cryptocurrency into circulation.
At the same time, as mentioned earlier, the locked coins act as a guarantee of the validators' honest and efficient performance. Validators receive rewards for good performance but may lose their locked funds if their work is subpar.
Staking vs. Mining
Many people have heard about mining as a way to generate new coins. But what are the differences between mining and staking? The key distinction lies in the consensus algorithms used in the chains where mining or staking can be applied. Mining relies on PoW (Proof-of-Work), while staking uses PoS (Proof-of-Stake).
Another difference is the required equipment. Mining demands significant computational power, whereas staking does not. This makes staking a more accessible way to earn profits.
Key differences between staking and mining:
| Parameter | Proof-of-Stake | Proof-of-Work |
| New block creation | Locking tokens | Performing computations |
| Expenses | Buying tokens | Buying equipment |
| Environmental impact | More eco-friendly | Less eco-friendly |
| Technical skills | Minimal | Required |
As the table shows, staking is a simpler and more environmentally friendly way to verify transactions and add new blocks to the chain. For this reason, modern blockchains increasingly use this method for generating new coins.
Moreover, PoS offers extensive scalability opportunities. It enables parallel processing of multiple operations, allowing PoS-based chains to handle tens of thousands of transactions per second.
Mining has become difficult for individuals due to the high cost of equipment and competition with large pools and mining farms. In contrast, the initial investment for staking depends solely on the price of the coins. You can choose inexpensive coins and start earning.
Another advantage of staking is that the earnings from locking coins in your account can be reinvested. This increases your stake and, consequently, your chances of adding new blocks, leading to a steadily growing potential income.
How to start staking
If you are interested in cryptocurrency staking based on the information above, here are the steps to get started:
First, choose a token for investment. Assess the coin from various perspectives. Does the project support staking? What is the token price? How many coins are required to stake? What is the minimum lock-up period, and what are the other terms? This will help estimate the actual costs and potential earnings.
Second, buy the selected cryptocurrency. Purchase the required amount of the chosen currency. After that, decide on the staking platform and method. Tokens are typically bought on exchanges using fiat money or other digital currencies.
Most staked coins are stored in a dedicated wallet, either software-based or hardware-based. Storing tokens in a hardware wallet is called "cold storage" because such wallets are not connected to the Internet, making them more secure against hacking.
Alternatively, coins can be staked directly on the exchange where they were purchased or on specialized staking platforms. For this option, you simply transfer tokens to a specified address.
If you do not plan to run your own validator node, you can delegate your tokens to another validator. When the validator receives rewards, they are distributed among all users who delegated their tokens.
If your funds are insufficient to stake independently, you can join a staking pool. These pools combine the capital of multiple users to earn rewards together. We will discuss staking pools in detail in the next section.
Staking pools
Staking pools allow multiple users to combine their resources for staking, offering a more reliable, efficient, and quicker way to earn profits compared to staking individually. This approach also eliminates the need to understand the complex technical details of the staking process.
Coin holders pool their resources to increase their chances of generating a new block and earning rewards. The total reward is then distributed among the participants based on their contribution to the pool.
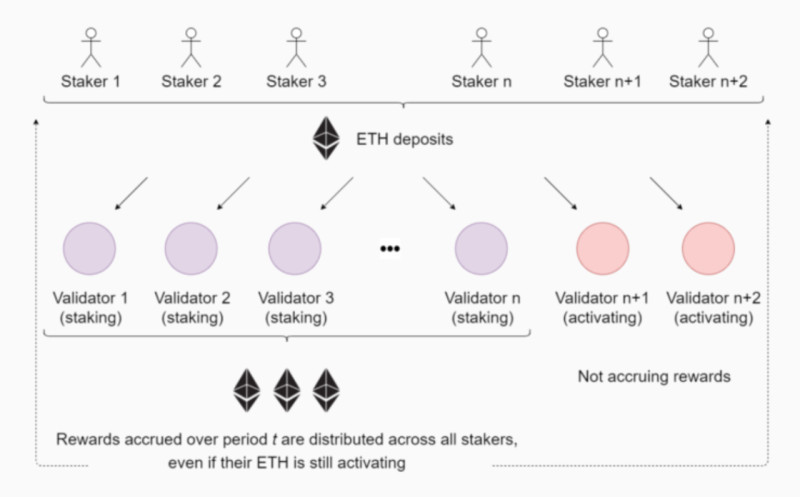
However, it is important to carefully choose the pool before joining one. Pay attention to the following criteria:
- Server stability.
The pool's servers must operate without interruptions. Unstable servers can hinder the pool's ability to perform its functions and complicate the withdrawal of funds in the future. - Fee structure.
Pools charge a percentage of the rewards earned from block creation, typically between 2% and 6%. Fees lower than 2% or higher than 10% should raise concerns. - Pool size vs. reward distribution.
Smaller pools offer larger potential rewards per participant but have lower chances of generating new blocks. Larger pools, while more likely to earn rewards, distribute them among more participants. Finding a pool with an optimal size and reward ratio is crucial.
Each pool has an administrator who manages validator operations and supports participants. Some pools require users to transfer their coins to a third party for storage, but others allow storage on cold wallets for added security.
The main advantages of such groups are stable income and a low entry threshold. There is no need to invest large amounts. However, there are also drawbacks. The main one is the need to share rewards with other pool members.
Liquid staking
We have often discussed that staking cryptocurrencies essentially means "freezing" the investor's funds, making them unavailable for other purposes. However, there is an option where staked coins can also work in other areas.
This is called liquid staking. Its essence lies in the fact that, in exchange for tokens locked in staking, the user receives "derivative" coins as collateral for the invested funds. These coins can be used for other operations within decentralized finance.
Such tokens, known as receipts, confirm that the user has staked their coins. They provide instant access to the user's funds without the need for unlocking them and allow participation in other DeFi protocols to earn additional income.
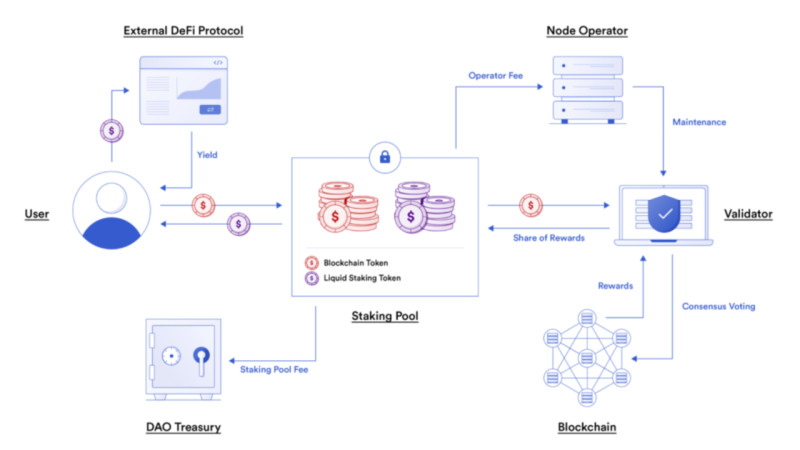
Liquid staking is essentially an improved version of classic staking. It is called "liquid" because it offers additional opportunities and flexibility for users who lock their assets. It enables investors to earn staking rewards while also engaging in other operations.
To participate in this type of staking, the user needs to deposit funds on a specialized liquidity platform, which securely verifies and stores them. These crypto assets are locked, and in return, LST (liquid staking tokens) are issued. These tokens can be used like any other digital currency—for trading, exchanging, and so on.
When a user wants to withdraw their staked assets, they must redeem the LST previously received to retrieve the tokens that were initially staked. This feature significantly enhances the efficiency and appeal of staking.
Advantages and disadvantages of staking
Like any other method of earning from digital currencies, cryptocurrency staking has its pros and cons. Let us take a closer look at them in this section.
Advantages of staking
- Passive income. Staking requires almost no active effort. You simply need to buy coins, lock them in your account, and earn rewards.
- This earning method suits many users, as it does not require significant initial investments. You can choose inexpensive cryptocurrencies for staking or join a pool to earn income that way.
- A pleasant bonus can include participating in airdrops conducted by developers of new digital currencies. They may reward users who stake on blockchains hosting their new tokens.
- Eco-friendliness. Compared to mining, staking is far less harmful to the environment. It requires fewer computing resources and, consequently, less energy.
- High returns. Some blockchains offer annual yields of up to 20%, which is difficult to achieve through other methods, especially without active participation.
Disadvantages of staking
- Locked funds. Staked funds are "frozen" and cannot be used for other purposes during the staking period.
- Price volatility. While your funds are locked, the value of the cryptocurrency can fluctuate significantly, not always in your favor. If the price drops, staking rewards may not compensate for the loss.
- Users risk encountering fraudulent projects and investing in fake blockchains. It is crucial to thoroughly research projects and check reviews before investing.
- Hacking risks. Decentralized services are vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could lead to fund losses. Unlike bank deposits, staking investments are not insured.
Conclusion
This article covered one way to earn passive income from digital currencies—cryptocurrency staking. The core idea involves locking a specific amount of platform tokens in exchange for rewards.
The rewards are paid in the same coins, introducing additional units into circulation. Stakers may also qualify to become validators, confirming transactions and adding new blocks to the network.
If a user does not wish to act as a validator or lacks sufficient capital, they can delegate their tokens to another validator or join a staking pool. In such cases, they receive a proportional share of the rewards.
Funds committed to staking ensure the validator’s effective and responsible operation. Misconduct or adding false data to the chain may lead to the total loss of staked assets.
You can also read:
- Types of cryptocurrencies
- Scalping in crypto trading
- Crypto listings
- Crypto processing
- Fear and Greed index in crypto
- Crypto lending
- Crypto nodes
- Volatility in crypto trading
- Funding in crypto trading








 Back to articles
Back to articles



